Cooperative Working Characteristics of Hydraulic Pumps and Hydraulic Motors
 Posted on 19/08/2024
Posted on 19/08/2024
Assume that there is no leakage and pressure loss in the system, and the efficiency loss is also ignored. The pressure at the pump suction port and the motor discharge port is zero.
Q=qn n=Q/q
M=pq/2π
N=Mn
Where: Q——the output flow of the pump or the input flow of the motor
q——the displacement of the pump or the motor
n——the speed of the pump or the motor
M——the input torque of the pump or the output torque of the motor
p——the output pressure of the pump or the input pressure of the motor
N——the power of the pump or the motor
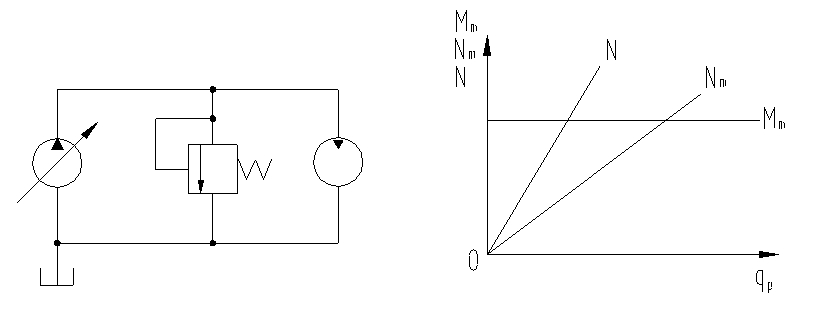
1. Working characteristics of variable pump and fixed motor speed regulation
When regulating the speed, the displacement qp of the pump needs to be changed. The larger its value, the larger the pump flow Qp. Since the motor displacement qm remains unchanged, the speed increases accordingly. The larger the pump pressure p depends on the adjustment pressure of the safety valve, which is a constant. Therefore, the output torque Mm of the motor is also a certain value, that is, no matter how the speed changes, its torque is constant, and its power is also variable, increasing with the increase of the speed. This system has a large speed regulation range and is suitable for systems requiring constant torque, such as metal cutting machine tools.
2. Working characteristics of fixed displacement pump and variable speed motor
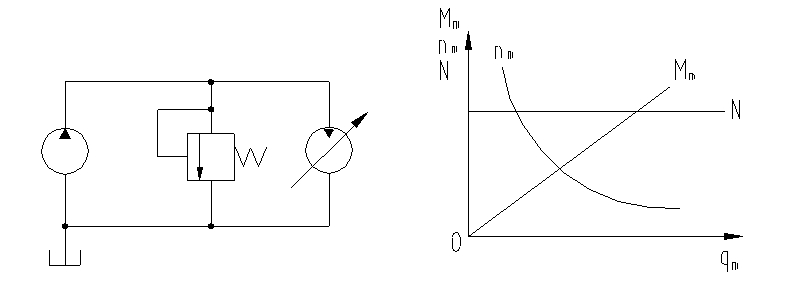
The pressure and flow rate of the pump remain unchanged, the motor speed nm is inversely proportional to the displacement qm, and the output torque Mm is proportional to the displacement qm. As the displacement qm increases, the speed nm decreases and the torque Mm increases, but it has no effect on the power of the motor, that is, no matter how the motor speed and torque change, its power is constant.
3. Working characteristics of variable speed pump and variable speed motor
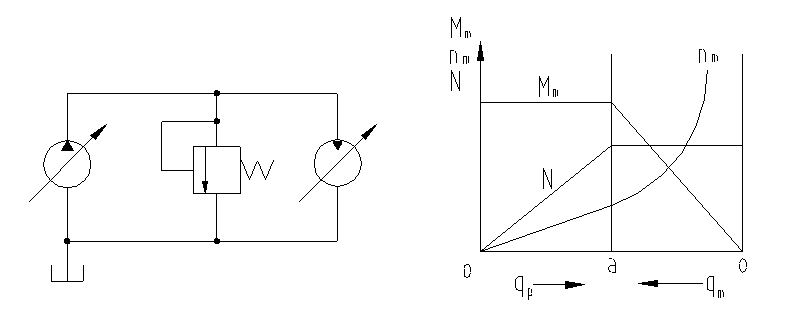
When the motor displacement qm is adjusted to the maximum, the motor speed nm is adjusted by adjusting the pump displacement qp, and its characteristic curve is as shown in the left half of the figure above, which is the constant torque adjustment area; when the pump displacement qp is adjusted to the maximum value, the speed is increased by reducing the motor displacement qm, and its characteristic curve is as shown in the right half of the figure, which is the constant power adjustment area. Point a is the transition point between the two areas, where the displacement of the pump and the motor are both adjusted to the maximum. This system has a large speed regulation range, and the constant torque and constant power characteristic areas can be freely selected.
